Mobile applications on AWS
ABOUT VITRUVIAN
Vitruvian has built platforms that automate business functions of real estate companies using real estate management software real estate websites and mobile apps, thereby allowing them to scale their business and manage growth effectively. It’s digital platform attracted more than 2 lakh properties spread across more than 1000 customers across the country.
THE CHALLENGE
Vitruvian launched the real estate website, real estate software, real estate CRM, real estate ERP to serve the customer. With the business growth, they needed the speedy and automated way of deployment cycle which would help them to move the software releases across the different environment (Dev, Staging, UAT etc.) and once accepted the need to push to production.
Since the market is volatile and there are new requests coming every now and then the manual deployment process was becoming a nightmare and delivery timelines were getting missed at times.
With the increase in the load, the existing application design was failing to serve request at scale. Security policies are not followed and thus Vitruvian wanted Techpartner to fix this loophole.
SECURITY LAPSES
● Existing Infra is running under default VPC
● All the instances which are launched are with public IP attached to it including DB instance
● SSH and DB ports were found open to the world (0.0.0.0/0) and all the Web and App instance talking to DB on the public IP
● No specific rules are created in the database
● AWS root access is shared with leads
● The root key is used to access the S3 from app instance for backup
● DB credentials policy is not set (it was taking password even with a single character)
● On app server Tomcat manager is open to the world
● To access the instance single on-pem file which is created during the launching of instance is shared across all developers
● PEM Files are not rotated
DEPLOYMENT LAPSES
Deployment is manual. The Dev team access both web and app server for the deployment and do the git pull there. There were cases where for hotfixes were done directly on the production and related changes are not push to the repository and thus at some point track is missing.
Since deployment is done manually Dev team was given the access to production servers and databases.
PROPOSED ARCHITECTURE
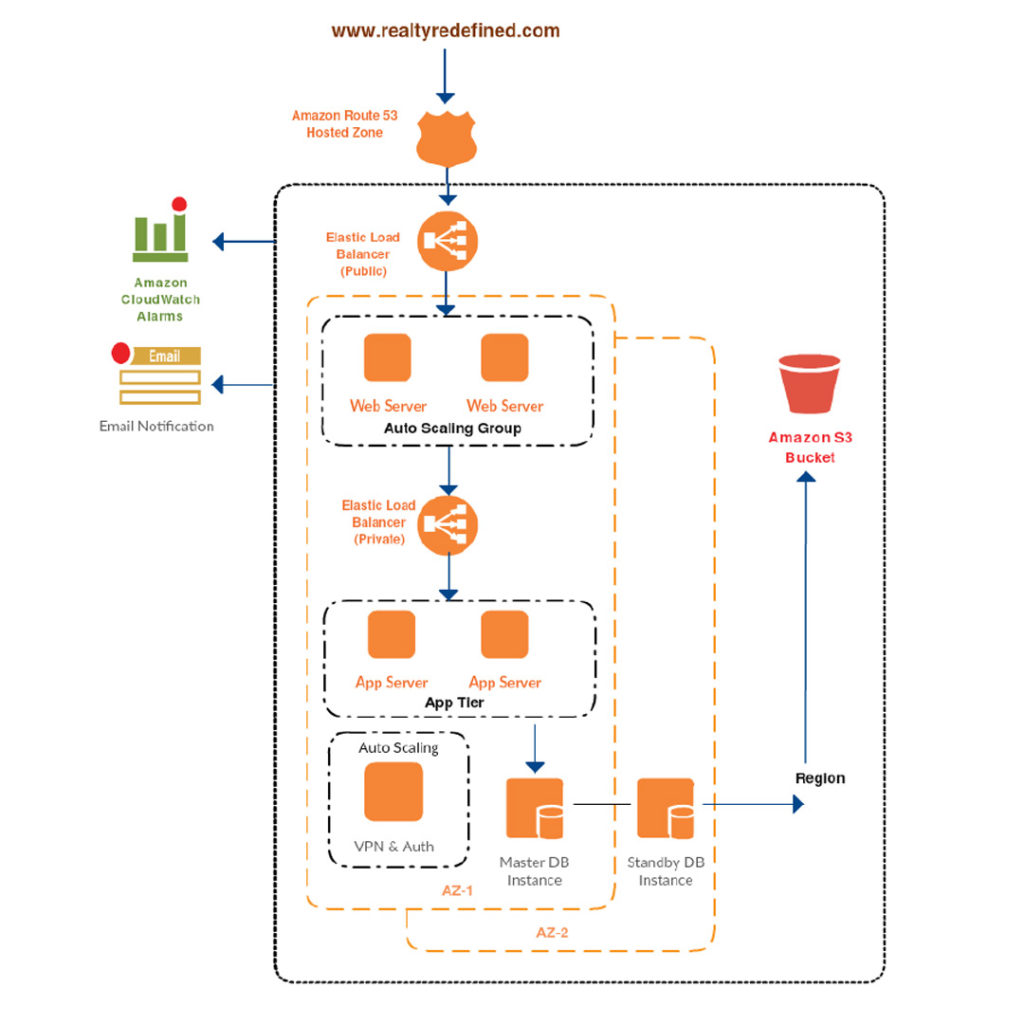
INSIGHT ACTION
The Techpartner team worked with developers to understand the process. Together we chalked down the plan for the automated deployment. Our more focus was to utilise the more open source tools and achieve the required output. Using Ansible we automated the deployment on multiple servers. With the help of Jenkins and Selenium created the Job which will do the post-deployment tests and certify the build. On successful completion of Jenkin jobs, we gave the option either to automatically push the code on production at the scheduled time or do it manually whenever hotfix is needed. With this deployment process, Vitruvian was able to deploy the scalable architecture in minutes.
The Techpartner team also suggested that how we can split the infrastructure into micro services so as to catered the increasing requests which can handle the load easily.
While working on elimination SPOF we not only added the additional systems but also made sure that there won’t be additional outflow in billing and that is controlled by using auto scaling for scaling in and out.
SECURITY BEST PRACTICES
To overcome the existing lapses in the security we redesigned the AWS architecture and implemented best security practices as per AWS standards.
● New 3-Tier VPC. (Public, Private & DB Subnet) with separation of staging and testing environment.
● IAM Role to instance for S3 access
● IAM User for AWS Console access with MFA enabled with restricted policy access.
● Password policy across entire Infra (Web, APP & DB) as well as in IAM.
● Except for Public Facing load balancer everything taken under Private and DB Subnet and thus no instance except VPN Server (Jump host) having public IP.
● VPN server provided with LDAP as an authentication server and all other instances are configured as a client so that PEM file sharing is no more needed.
● PEF files are rotated after every 3 months and kept only with ‘admin’ user and not with ‘group’.
● Root key reference is deleted from every environment.
● Application changes were made to point local DB IP.
● Except port 80 and 443 for web and 1194 for VPN nothing is publically open
DEPLOYMENT AUTOMATION
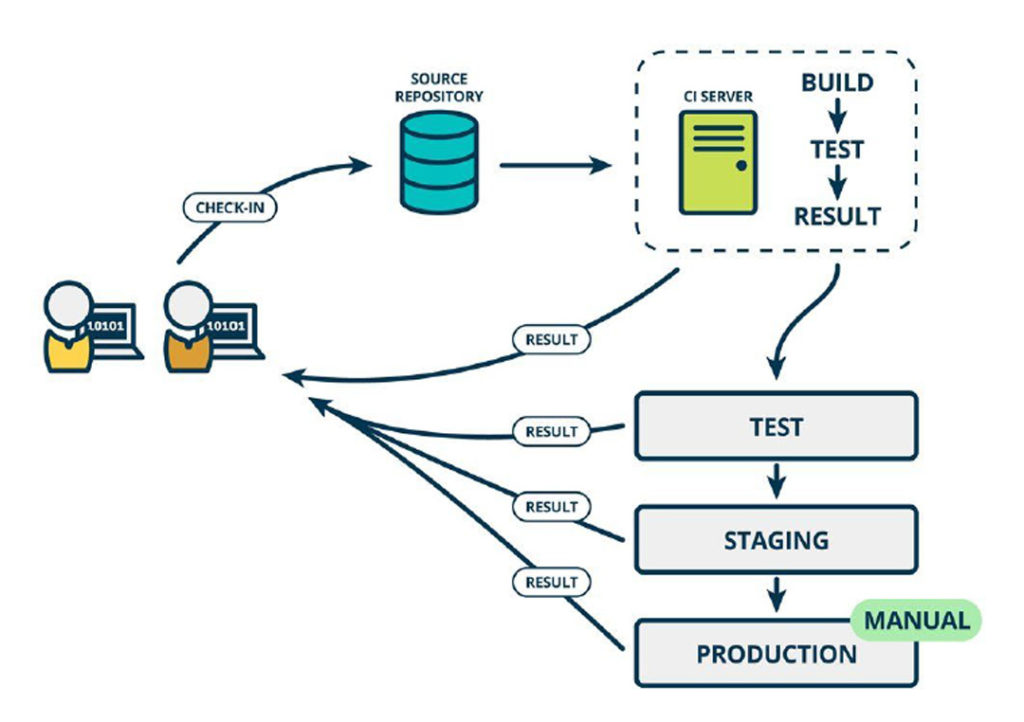
Deployment is automated for TEST and STAGING environment and kept either scheduled or manual for production. This has been achieved by configuring the automation tools Ansible & Jenkins. Selenium test cases were executed during every code change and on success, build were push to TEST or STAGING environment automatically once build is certified and ready to push to production.
Jenkin is configured either to run the job manually or to schedule the deployment job at night which automatically pushes the build to the production server and intimate the team once it is successfully done over Email.
Every newly launch server by auto-scaling is getting registered with Ansible and deregistered when scaling down to maintain the deployment across all the servers.
THE BENEFITS
● Scalable Architecture: With the scalable architecture Virtuvian was able to serve the client with improved response time which in turns helped to acquire more clients.
● Performance: As the application became modular the whole CI/CD process became easy and efficient.
● Automation: Automation reduced the manual deployment time by 90% giving free hand to the developer to concentrate on innovation.
AWS Stack
For the success of the project, Techpartner used the below AWS Services…
● Amazon EC2 was used to compute with a combination of on-demand and reserved instance. Instances were configured to spin up automatically during load.
● Amazon S3 was used to store mainly for the images which need to be accessible across the instance
● AWS NAT Gateway Service was used to provide the Internet to systems in private subnet during patch management
● AWS CloudWatch was used to monitor the instance performance
● AWS CloudTrail was used to keep track of the activity across the AWS Environment
● AWS CodeCommit was used to keep track of the code repository
● AWS CloudFormation was used to templatize the infrastructure footprint
● AWS Inspector was used to check application and OS security and apply fixes as recommended and ensure consistency
● AWS Config was used to track changes for AWS resources and also to alert with resources that are not compliant as per defined rules
● AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) was used to provide AWS resources access as per the company’s policy. Also wherever possible IAM roles were used to provide access to AWS resources as per IAM’s best practices
For more, visit www.techpartneralliance.com or contact us at info@techpartner.in.



